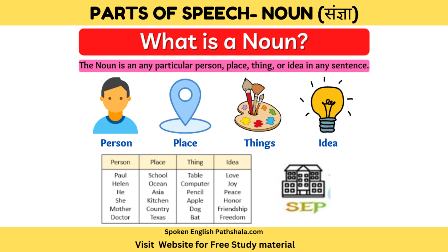
welcome to our detailed exploration of nouns, a fundamental part of grammar. Whether you're a student, a writer, or simply interested in language, understanding nouns is crucial for mastering...

Possessive nouns are nouns that show ownership or a specific relationship between one thing and another. They are used to indicate that something belongs to someone or something. How to Form...

Compound nouns are nouns that are made up of two or more words combined together to form a single noun with a specific meaning. These words are often joined together to create a new term that...

Uncountable Nouns: These cannot be counted individually and typically refer to substances, concepts, or mass entities. Examples include: Substances: water, sugar Concepts: information, advice...

Countable Noun: These can be counted and have both singular and plural forms. Examples include: Singular: book, apple Plural: books, apples गिनती योग्य संज्ञाएँ...

Collective nouns denote groups of people, animals, or things considered as a single unit. Examples include: People (व्यक्ति): team, family Animals (जानवर): herd, flock Things...
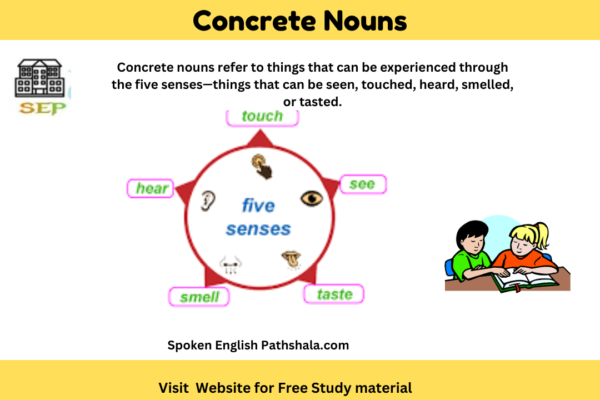
Concrete nouns refer to things that can be experienced through the five senses—things that can be seen, touched, heard, smelled, or tasted. Examples include: Objects (वस्तुएँ):...

Abstract nouns represent ideas, qualities, or conditions that cannot be perceived with the senses. Examples include: Ideas (विचार): democracy, freedom Qualities (गुण): bravery,...

Common nouns refer to general items or concepts and are not capitalized unless they start a sentence. Examples include: People (व्यक्ति): teacher, student Places (स्थान):...

Proper nouns name specific individuals, places, or organizations and are always capitalized. Examples include: People (व्यक्ति): Albert Einstein, Marie Curie Places (स्थान):...
